Sprague Regulatory Matters is provided as a courtesy to our customers. Please note that the information contained in Sprague Regulatory Matters is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal or business advice on any subject matter. You should not act or refrain from acting on the basis of any information included in this without seeking legal or professional advice.
Natural Gas Fires Electric Generation During Summer Heat Waves
New England – Electric & Natural Gas
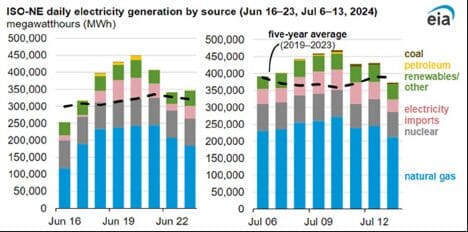
Electricity generation increased in New England to meet the additional air-conditioning demand during heat waves in June and July. Natural gas-fired electricity generation made up 56 percent of New England’s generation mix during the week of the June 16th heat wave, peaking at 61 percent on June 22nd. Between July 6th and 13th, natural gas-fired electricity averaged 58 percent of the generation mix (Natural gas-fired electricity generation increased during heat waves in New England – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)). Despite the closure of the Mystic Generating Station in Massachusetts, natural gas accounted for more of the generation mix during both periods compared with the five-year (2019–2023) average of 48 percent.
Tioga Pathway Expansion Project
Pennsylvania – Natural Gas
National Fuel Gas submitted an application seeking Federal Energy Regulatory Commission approval for the Tioga Pathway expansion project in north-central Pennsylvania. The project, with a planned in-service date of November 1, 2026, would add 190,000 dekatherms per day in capacity and has an estimated ost of over $100 million. This would provide firm transportation capacity for Marcellus and Utica shale production in Tioga County, Pennsylvania, to various downstream markets and connections with the interstate systems of Tennessee Gas Pipeline and Transcontinental Gas Pipe Line.
Northeast States Collaborative on Interregional Transmission
Northeast – Electric
onnecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, and Vermont entered into an agreement (Northeast States Collaborative on Interregional Transmission – Johns Hopkins – Ralph O’Connor Sustainable Energy Institute (jhu.edu)) to coordinate on transmission grid expansion efforts in conjunction with the U.S. Department of Energy. Three main aspects include: (1) Identifying shared transmission priorities and integrating them into regional transmission planning processes; (2) Federal policy and programmatic support is desirable to facilitate regional and interregional transmission planning for offshore wind and other clean energy objectives; and (3) The establishment of common technical standards for offshore wind transmission facilities that could reduce the cost of meeting federal and state offshore wind goals and ensure current transmission procurements are compatible with future interregional transmission projects.
The Future of Natural Gas
Illinois – Natural Gas
The Illinois Commerce Commission commenced proceedings to evaluate the future of natural gas (Future of Gas Proceedings (illinois.gov)) as it transitions away from natural gas use for heating and other end uses. Commission staff are recommending that the second phase be delayed by a year; however, the commission is reluctant to approve the change. Initially, the commission saw phase two of the future of gas workshops concluding by July 2025, but under the staff recommendation, it would run through July 2026. The major hurdles include identifying building decarbonization pathways, the relative cost of each pathway, the pace of transitioning major infrastructure systems, and establishing an equitable transition.
Examining Customer Enrollment
Maine – Electric
The Maine Public Utilities Commission commenced a proceeding to evaluate the timing for enrollment and unenrollment from a competitive electric provider (CEP) or standard offer service (SOS) provider. The commission is conducting this proceeding as the result of a legislative effort and is seeking comment on the following: (1) Is it feasible to effectuate a customer’s request to enroll or unenroll with a CEP or SOS provider within three business days? (2) Should a requirement that a customer be enrolled or unenrolled with a CEP or SOS provider within three business days apply to customers in all rate classes? (3) Does enrollment or unenrollment in the middle of a billing cycle, where a customer may receive prorated bills, create an unreasonable administrative burden or any unintended consequences? (4) Should the number of times a customer can enroll or unenroll with a CEP or SOS provider be limited? The commission is required to file a report with the Maine Legislative Joint Standing Committee on Energy, Utilities and Technology by February 1, 2025.
Utilities and Large Power Users
Virginia – Electric
The Virginia State Corporation Commission scheduled a technical conference for December 2024 to explore the effects of the increasing number of large-use retail electric customers on Virginia’s utilities, ratepayers, and power grid. The proceeding will consider current and future challenges presented by the growth of such hyperscale power users across the Commonwealth. Large power users such as data centers could bring an unprecedented amount of new load for electric utilities, creating complications and risks the utilities have not previously encountered. The technical conference is intended to identify potential frameworks that facilitate service; address risks and issues of the increased usage; are just and reasonable to current and future customers; and meet current Virginia statutes. In addition, this proceeding may examine issues related to the co-location of generation resources at new large-use customer load sites. Three main questions to be addressed include: (1) Should the commission establish a tariff framework and terms of service for these large-scale customers? (2) Should certain transmission costs be directly assigned to a new large-use customer class? (3) Should certain generation costs be directly assigned to a new large-use customer class?
Energy Fund to Finance Generation Projects
Texas – Electric & Natural Gas
The Texas Public Utility Commission selected 17 natural gas power plant projects that will receive government financing totaling about $5.4 billion. The commission approved the proposals for power plants capable of generating enough electricity to power 2.4 million homes. If the companies prove their projects are viable, they will receive three percent loans from the taxpayer-funded Texas Energy Fund. The Texas Legislature created the fund in 2023 to finance about 10 gigawatts of electric generation capacity to reinforce the Texas (ERCOT) power grid. This is one of a number of legislative directives since the power blackouts of the 2021 winter storm.
Disclaimer of Liability
Every effort is made to provide accurate and complete information in Sprague’s Regulatory Matters. However, Sprague cannot guarantee that there will be no errors. Sprague makes no claims, promises, or guarantees about the accuracy, completeness, or adequacy of the contents and expressly disclaims liability for errors and omissions in the contents of this update.
Neither Sprague, nor its employees make any warranty, expressed or implied or statutory, including but not limited to the warranties of noninfringement of third-party rights, title, and the warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose with respect to content available from Regulatory Matters. Neither does Sprague assume any legal liability for any direct, indirect or any other loss or damage of any kind for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, product, or process disclosed herein, and does not represent that use of such information, product, or process would not infringe on privately owned rights.
The materials presented in Regulatory Matters may not reflect the most current regulatory or legal developments, verdicts, or settlements, etc. The content may be changed, improved, or revised without notice.
Copyright Statement
All content within Sprague Regulatory Matters is the property of Sprague unless otherwise stated. All rights reserved. No part of Regulatory Matters may be reproduced, transmitted, or copied in any form or by any means without the prior written consent of Sprague.









